The appearance of flesh-colored cone-shaped growths in the genital area is a cause for concern, which is fully justified, since the health of the genital area is an important point for the overall physical and moral well-being of a person.
These warts cause discomfort, interfere with normal sex life and can cause more serious health problems. If the integrity of the condylomas is violated, an infection may occur and a transition to a malignant entity may occur. Therefore, the desire to get rid of such manifestations is understandable and quite natural.
Reasons for the appearance
The causative agent of papilloma warts is the human papilloma virus. This virus contains a specific DNA set that successfully integrates into the cells of the human body and causes them to change their developmental cycle, shape and structure.

According to the International Classification of Diseases ICD-10, human papillomavirus is coded B97. 7. Anogenital warts of a venereal nature are indicated by code A63. 0.
There are many different strains of this virus, each of which causes specific wart papillomas. The type of virus determines the course of the pathological process, the symptoms, the localization of the manifestation and the severity of the complications.
Strains are divided into two main types:
- cutaneous, with predominant occurrence on the dermal layer;
- mucous membranes that appear on the mucous epithelium of the genital organs, oral cavity, etc.
In addition, papillomavirus types differ depending on the risk of degeneration into an oncogenic process into oncogenic, moderately oncogenic and non-oncogenic.
Most often, several different strains are present in the body of an infected person at the same time.
Routes of infection and risk factors
There are several ways for the pathogen to enter the body:
- "Vertical" transmission. This is called the transmission of an infectious agent from mother to child during pregnancy. Currently, it is not known whether the infection occurs in the prenatal period or directly during childbirth, but it is undesirable to perform a cesarean section on a mother with papillomavirus. Cesarean section is selected only in case of bleeding papillomas inside the birth canal.
- Sexual path.The infectious agent can enter the body during vaginal, oral or anal sex. The pathogen is also transmitted through saliva during a kiss. Using a condom during intercourse does not guarantee protection against the virus, but it does reduce the likelihood of transmission.
- Household way.This mechanism of disease transmission is quite rare. Infection can occur through contact with the patient's personal belongings. Since the virus is contained in saliva and urine, it is possible to get infected by using other people's dishes, shared towels, personal hygiene items, from the edge of the toilet or in the bathroom.
The mode of infection is determined mainly by the age of the person: in infants, with a high degree of certainty, it can be established that the infection is from the mother, and in older children, through contact and household contacts. From the age of 17, in most cases, it becomes sexual intercourse.
According to statistics, the human papilloma virus is present in the bodies of more than half of the sexually mature population, but in most cases it does not manifest itself in any way and is present in the form of a carrier.
The peak of the disease occurs at a young age of 17 to 25 years. This is due to the maximum sexual activity and the high sensitivity of the epithelium on the organs of the genitourinary system.
Predisposing factors that increase the likelihood of the disease are:
- early onset of sexual activity;
- frequent change of sexual partners;
- age up to 25 years;
- sexual contact with people who previously had human papillomavirus or other sexually transmitted diseases;
- pregnancy;
- imbalance of intravaginal flora;
- any chronic disease;
- endometriosis;
- therapy with cytostatic or glucocorticosteroid drugs;
- Overweight;
- disruption of the thyroid gland and disruption of insulin production;
- hypovitaminosis.
Frequent stress and non-observance of the principles of personal hygiene significantly increase a person's chances of the infection going into an active phase after entering the body.
After introduction, the virus spreads throughout the body through the bloodstream, attaches to cells, penetrates their structure and integrates its DNA into the cell's DNA. After that, the affected cells begin to actively grow and divide, which is why condylomas appear.
Ways to develop
After entering the human body, the virus does not cause any symptoms for a certain period of time.
The course of the disease is carried out according to the following algorithm:
- Hidden period. During this stage, the carrier is not aware of the presence of an infectious pathogen, as there are no clinical manifestations. But at this stage, a person is already infected and can infect his partner through sexual contact. This latent period can last from 2-3 months to several years.
- The onset of the disease occurs when the virus multiplies sufficiently in the body or when the defense mechanisms of the immune system decrease. During this period the first symptoms appear.
- Active development with increasing symptoms.
The further course of events developed in one of the following directions:
- self-treatment with complete disappearance of papilloma warts (most often observed after the end of pregnancy);
- slow course and lack of growth of skin growths;
- active dynamics of papillomas with an increase in shape, size, number and fusion of closely located groups;
- degeneration of benign formations into malignant ones.
Types of condyloma
There are several conventional types of condyloma papillomas:
- exophytic- protruding above the surface of the skin or mucous membrane with preferential growth outside;
- endophytic- with predominant growth deep in the skin structures, therefore hardly noticeable during visual inspection;
- Buschke-Levenstein education- characterized by rapid growth rates, large sizes and frequent relapses after a course of treatment. In this form, both external growth and damage to the deep inner layers of tissue occur.
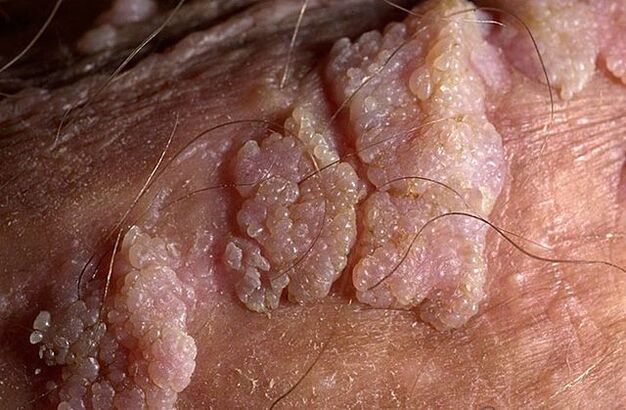
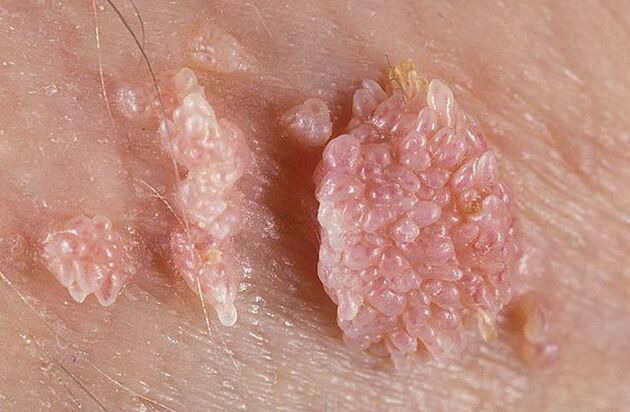
Genital warts can have a thin base or a wide base in shape. If the stem is thin, the tip may be pointed or club-like. Broad-based papillomas are quite rare. The color of all such growths is close to the color of the skin: from flesh to pink. The surface can be soft or covered with a layer of keratin.
Warts can appear singly or in nodule-like groups. Sometimes such multiple groups reach sizes of 1. 5 cm. When several groups merge, formations appear that resemble cauliflower inflorescences or a rooster's comb. These growths facilitate the identification of the disease during examination.
Single growths usually do not cause as much discomfort as large elements. In rare cases, they break and bleed slightly.
Large formations are more problematic: they can become wet, bleed and worsen due to a secondary infection that takes root in the affected areas.
Symptoms
The first symptoms appear after the end of the latent period, which in the shortest case lasts several weeks.
The appearance of condylomas occurs as follows:
- a slight redness appears on the skin, which begins to itch;
- a rash appears on the surface of the skin or mucous membrane in the form of blisters or small bumps;
- tubercles gradually increase to 1-1. 5 centimeters in length;
- New rashes appear nearby, which also turn into condyloma papules.
Localization depends on the specific strain and the place of entry of the pathogen into the body:
- external genitalia;
- anal area (anogenital papillomas);
- inside the urethra;
- on the cervix;
- on the epithelium in the mouth (on the buccal surfaces, tongue and inner side of the lips).
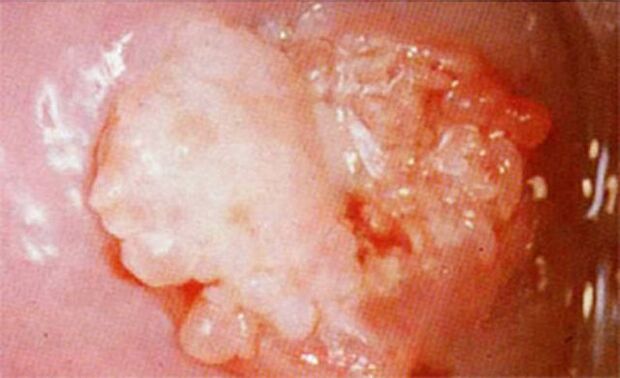
The clinical picture may differ in each individual case depending on the health status of the person. Small warts may not show any other symptoms.
In more severe cases, the following accompanying symptoms are observed:
- itching or burning at the site of the rash;
- sensation of a foreign object in the perineal area;
- humidity in the area of neoplasms;
- unpleasant smell from the place where the condylomas are located.
During physical activity, prolonged walking or running, all the above symptoms intensify.
In severe cases, fatigue, weakness, signs of intoxication, prolonged headache, fever and high fever are observed.
In men and women, the symptoms have some differences. This is due to anatomical differences and characteristics of sexual behavior.
Manifestations in men
Condylomas in men most often affect the scrotum, groin, pubis and various structural parts of the penis: head, body, frenulum and prepuce, coronal groove. When localized near the urethra, papillomas acquire a pronounced red color, and this location often causes splitting or splashing of the stream when urinating.
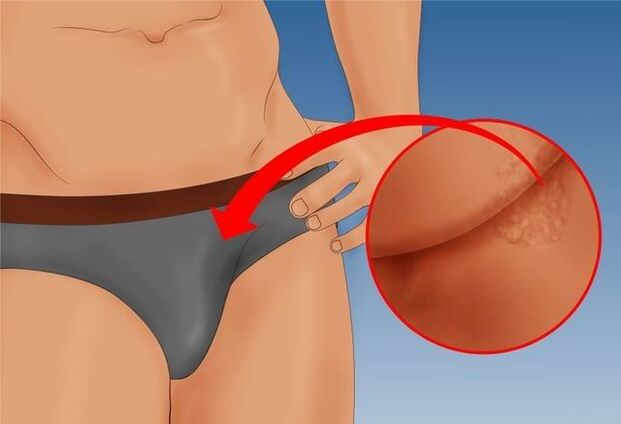
If the rash is located at the exit of the anus, severe pain may occur during defecation and there may be blood in the stool. Because of this, a reflexive fear of defecation often occurs, which causes periodic constipation and sometimes hemorrhoids.
Often there is a vague pain in the lower abdomen, during sex there is a burning sensation and pain, as well as when urinating.
Prolonged infection reduces a person's immunity, making them more vulnerable to respiratory diseases that are more difficult to treat than usual.
Manifestations in women
The most common places for the occurrence of papillomas in women are the perianal areas, where humidity and temperature are constantly elevated: the epithelium of the clitoris, the labia, the vaginal outlet and the opening of the urethra. If infection occurs during anal sex, a ring of growths may concentrate around the anus.
Large masses often become secondarily infected, causing a strong odor, bleeding, ulceration, and severe pain to touch. When walking there is irritation and severe discomfort.
In 50% of women, whitish elements are formed on the cervix, which are detected during a routine colposcopy, before which they are treated with an acid disinfectant, which can improve the white color of the warts.
In some cases, all growths are located on the mucous membrane of a woman's internal genital organs, so she does not notice them until a scheduled visit to the gynecologist. This is often why treatment starts later than in men.
Often, women experience discomfort due to the presence of formations in intimate places, which forces them to refuse sex.
Rarely, papillomas appear in the mouth, and in extremely rare cases - on the pubis, thighs, neck or face.
Features of condylomatosis during pregnancy
If condylomatosis has been treated, pregnancy should be planned no earlier than a few months. The period of abstinence from pregnancy is extended if the woman has taken antiviral drugs during treatment. After successful treatment and maintained interval, you can safely get pregnant.
If the disease was detected during pregnancy, then it is recommended to wait for treatment until all the baby's organs are already formed. Treatment after 28 weeks does not cause abnormalities in fetal development.
The reasons for the appearance of condylomatous warts in pregnant women include a standard decrease in immunity with increased stress on the body and significant hormonal fluctuations.

If the papillomas are located on the external parts of the genitals or in the perianal area and do not cause discomfort, then the question of treatment can be postponed until the birth of the child. But in case of rapid growth, increase in size and severe pain in growths, you should immediately consult a doctor. Sometimes, with a high rate of progression of the formations, their loosening is observed, which can lead to rupture of the vagina.
This disease, as a rule, does not affect the formation of the fetus, but its effect extends to the state of the mother and the birth process. If other infections are present, there is often a risk of premature birth.
When condylomas are damaged during the passage of the fetus through the birth canal, this often leads to infection of the baby and condylomatosis of the larynx in the neonatal or breast period. Therefore, the presence of significant papillomas in the birth canal is a direct indication for cesarean section.
If necessary, the growth is removed during pregnancy, after which the tissue is sent for histology to check its benignity.
The use of methods of traditional medicine to remove condylomas during pregnancy is unacceptable, as this may not only not have a positive result, but may lead to the degeneration of benign cells into malignant ones.
Formations that did not cause discomfort during pregnancy often disappear on their own without treatment within a few months after childbirth, as the woman's hormonal balance normalizes.
Diagnosis
If the patient notices symptoms reminiscent of the human papillomavirus, he should contact a gynecologist, urologist or venereologist.
First of all, the specialist conducts a survey to clarify the following points:
- time of detection of the first symptoms by the patient;
- probable causes of infection;
- dynamics and development of the disease until a doctor's visit.
After that, a clinical examination is performed, during which the specialist determines the location, intensity, size and condition of the growths. In women, additional colposcopy (examination of individual genital organs with magnification) or extended colposcopy (similar procedure with acetic acid solution) is performed.
For a more accurate diagnosis, the doctor prescribes the following additional tests:
- PCR diagnostics, allows you to detect the pathogen in scrapings from the epithelium of the affected areas and determine its quantity (it also allows you to determine the strain of the virus);
- anoscopy- visual inspection of the area near the anus with magnification;
- cytology and histologyfragments of formations to identify atypical cells or tissues;
- biopsy of growthsfrom epithelial tissues for microscopic examination of the tissue structure;
- antibody titer detectionto this virus;
- spreadfrom the cervical canal and cervix for microscopic oncocytology.
If necessary, consultations with a dermatologist or proctologist are scheduled. If the diagnosis is carried out on a pregnant woman, then it is necessary to contact an obstetrician-gynecologist.
After receiving all the necessary data, the specialist can choose an individual tactic for therapy and complete relief from the disease.
Treatment
Often with condylomatosis, people avoid visiting medical institutions and choose therapy themselves, preferring local drugs that can eliminate visible manifestations, but do not treat the body of the infection, transferring it to a latent stage. Such treatment almost always leads to relapse. Therefore, for a final cure, an integrated approach is needed, which can only be determined by a specialist.
Treatment is carried out in the following areas:
- removal of growths;
- fight the virus;
- strengthening the patient's immunity.
All methods used to combat genital warts are divided into radical and medicinal.
Radical methods
Such methods are chosen if it is necessary to urgently eliminate external manifestations or when condylomas are localized on the cervix in women.
The following methods are used for removal:
- Surgical excisionformations using a scalpel under local or general anesthesia. The incision site is sutured with surgical thread. Despite the fact that this method is considered classic, it often causes postoperative bleeding and long rehabilitation in the hospital, so recently surgical removal is used less and less.
- Cryodestruction with liquid nitrogen.This method is relatively cheap and safe and does not require anesthesia or anesthesia. After freezing, the protein of the formations is destroyed, the nodules dry up and fall off. After a few weeks, no scars or marks remain at the treatment site.
- Laser removal.Despite the safety and high efficiency, the method requires anesthesia and is characterized by a high cost, so it is prescribed if other methods cannot be used. When exposed to a laser beam, the structure of the growth stem is destroyed. After cauterization, the condyloma is deprived of nutrition, which within a few days leads to its necrosis and the scab disappears. Scars often remain after laser removal.
- Electrocoagulation.The method is affordable, but it is very painful, so it requires local anesthesia. Genital growths are exposed to high temperatures, at which papillomas are burned. The scabs fall off on their own after a few days, leaving behind scars.
- Radiosurgery.Currently, this is the most high-tech, fast and effective method, which determines its high price. With the help of high-frequency radio waves, genital warts are painlessly removed in 15-30 minutes. After such removal, there is no bleeding, healing occurs within a day, after which no traces remain on the skin.
- Destruction with chemicals.This technique is only suitable for small formations without multiple fusions. Special strong substances are used, which leads to the death of growth cells. These products are based on highly concentrated acids or bases that cause local chemical burns.
If we limit ourselves only to radical methods of combating condylomatosis, then the recurrence of condylomas occurs in every third case.
Drug therapy
The integrated approach includes eliminating benign formations, eliminating the virus in the body and increasing the immune status. Therefore, drug treatment includes the use of such drugs:
- Pharmacy productsfor wart necrosis, acceptable for home use. For several days, this product should be applied topically to the warts. If the drug gets on healthy tissue near the growth, a deep chemical burn will form, so you need to apply the drug very carefully. After daily applications, take a short break of a few days. If the shoot does not fall, then the course is repeated. Pharmaceutical products that cause growth necrosis include solutions and ointments.
- Antiviruses.They can be for local or systemic use.
- Immunomodulatorsto improve immunity.
In addition, to improve the body's defenses, a systematic intake of multivitamin complexes, a special diet and a healthy lifestyle are prescribed.
After treatment, immunity to condylomatosis does not develop, so re-infection from a previous sexual partner is possible.
Possible complications
If left untreated for a long time, condylomatosis causes the following complications:
- The attachment of bacterial infection to the damaged condylomatous papillomas, which leads to purulent formations, balanoposthitis and ulcers in the perianal area.
- Viral-bacterial urethritis can develop when growths in the urethra lead to problems urinating, retention of urine in the body, and urinary tract infection.
- When large formations are located in the anus, hemorrhoidal bleeding and paraproctitis appear.
- Genital warts can affect a person's sex life, causing them to refuse sexual contact. All this often leads to depression and psychological problems.
- Women can develop cervical erosion and dysplasia.
- The greatest danger is the risk of degeneration of benign tumors into cancer (cancer of the head of the penis or cervix).
Precautions
Prevention of condylomatosis is divided into specific and general.
Specific preventive measures include vaccination with a new tetravalent vaccine. These vaccines do not work against all strains of the human papillomavirus, but they successfully fight the most dangerous of them, which cause cervical cancer. Vaccination is carried out from the age of 11 and is repeated three times.
Non-specific prevention is similar to the measures inherent in many sexually transmitted diseases:
- use of barrier contraceptives;
- personal hygiene at the right level;
- regular sexual partner;
- regular examination by a gynecologist or andrologist;
- timely treatment of diseases of the pelvic organs;
- refusal of alcohol and smoking.
In addition, it is necessary to avoid stress, physical fatigue, hypothermia and any factors that weaken the immune system. A healthy diet, improved health, and proper sleep patterns will help prevent genital warts.













































































